
SHIFT+F8 enables you to add a non-adjacent cell or range to a selection of cells by using the arrow keys.ĬTRL+F8 performs the Size command (on the Control menu for the workbook window) when a workbook is not maximized.ĪLT+F8 displays the Macro dialog box to run, edit, or delete a macro.Ĭalculates all worksheets in all open workbooks.į9 followed by ENTER (or followed by CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER for array formulas) calculates the selected a portion of a formula and replaces the selected portion with the calculated value. In extend mode, EXT appears in the status line, and the arrow keys extend the selection. Use the arrow keys to move the window, and when finished press ESC.
Note When the task pane is visible, F6 and SHIFT+F6 include that pane when switching between panes.ĭisplays the Spelling dialog box to check spelling in the active worksheet or selected range.ĬTRL+F7 performs the Move command on the workbook window when it is not maximized.
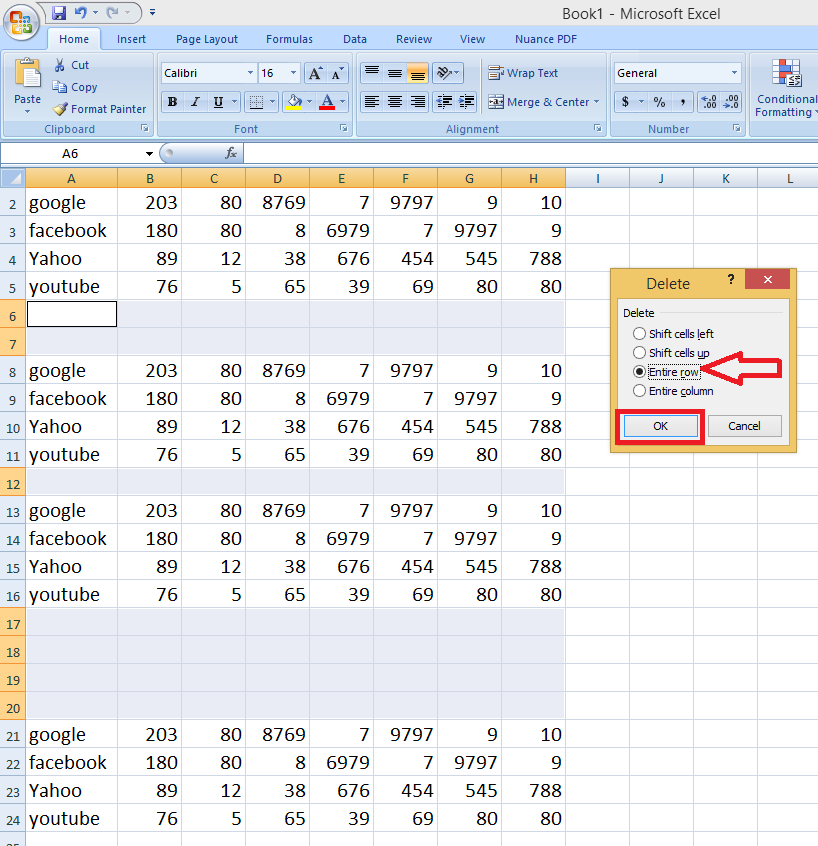
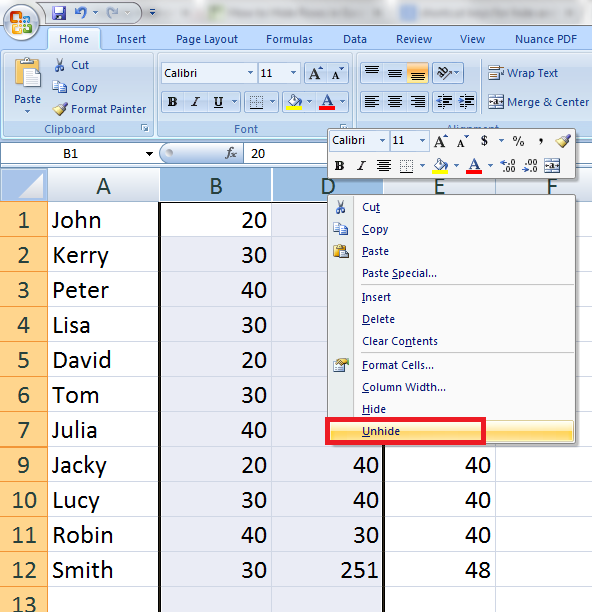
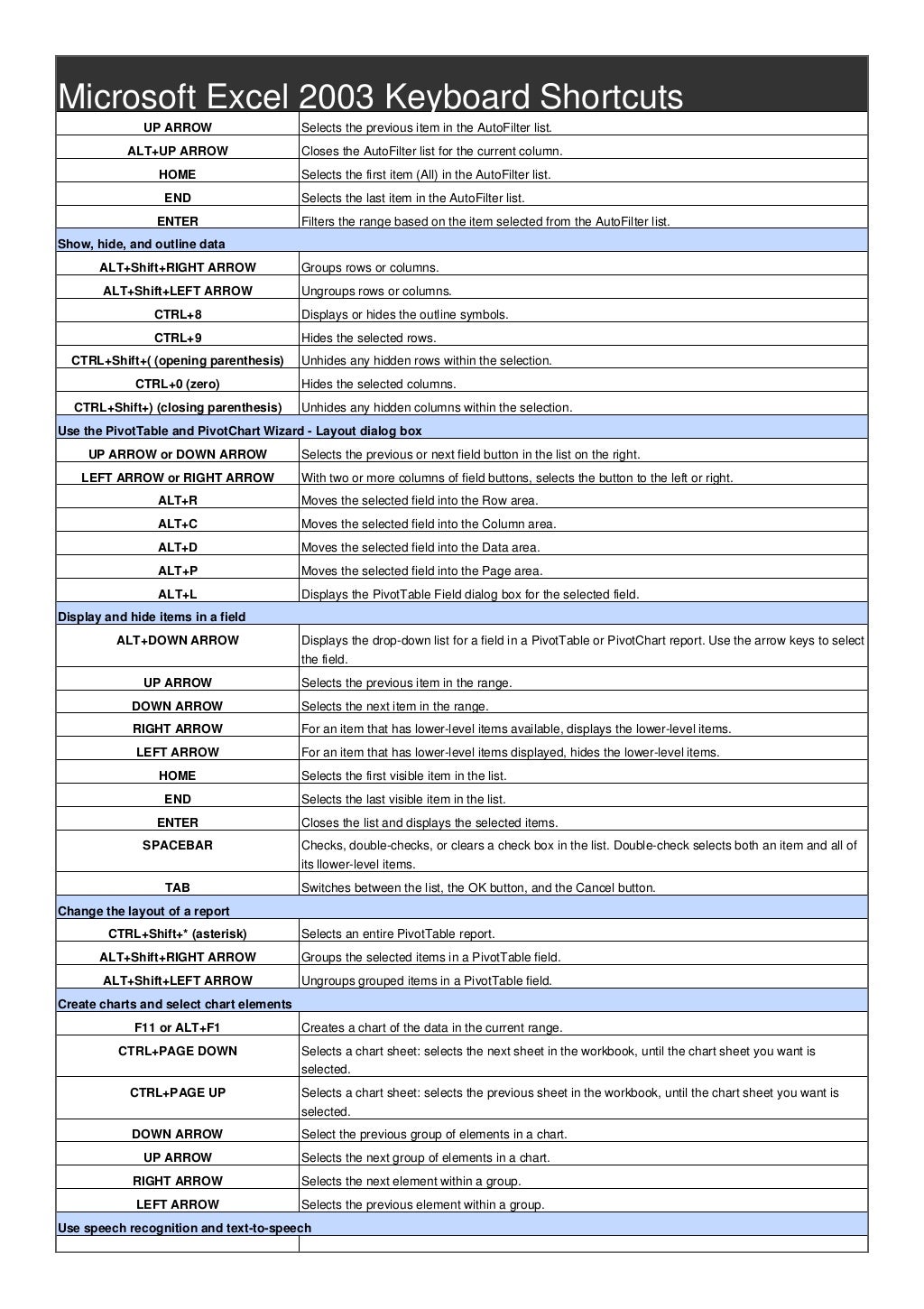
SHIFT+F6 switches to the previous pane in a worksheet that has been split.ĬTRL+F6 switches to the next workbook window when more than one workbook window is open. Switches to the next pane in a worksheet that has been split ( Window menu, Split command). Repeats the last command or action, if possible.ĬTRL+F4 closes the selected workbook window.ĬTRL+F5 restores the window size of the selected workbook window. SHIFT+F3 displays the Insert Function dialog box. It also moves the insertion point into the Formula Bar when editing in a cell is turned off. Below are the Microsoft Excel 2003 Keyboard Shortcuts for Function Keys:ĬTRL+F1 closes and reopens the current task pane.ĪLT+F1 creates a chart of the data in the current range.Įdits the active cell and positions the insertion point at the end of the cell contents.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
